Difference between on grid and off grid inverter
Introduction
Difference between on grid and off grid inverter: Simply install a solar energy system in your house. The panels are prepared, but the inverter is still a critical part. Sunlight is transformed into useful electricity by this unsung hero, but there’s a catch: not all inverters are made equal. Your solar experience can be made or broken by your decision between an off-grid and an on-grid inverter.
We’ll plainly describe the key differences between off-grid and on-grid inverters in this post. You’ll leave knowing accurately which inverter best fits your needs, whether you’re a cabin owner looking for energy independence or a city dweller connected to the utility grid. Let’s get started.
What is an On-Grid Inverter?
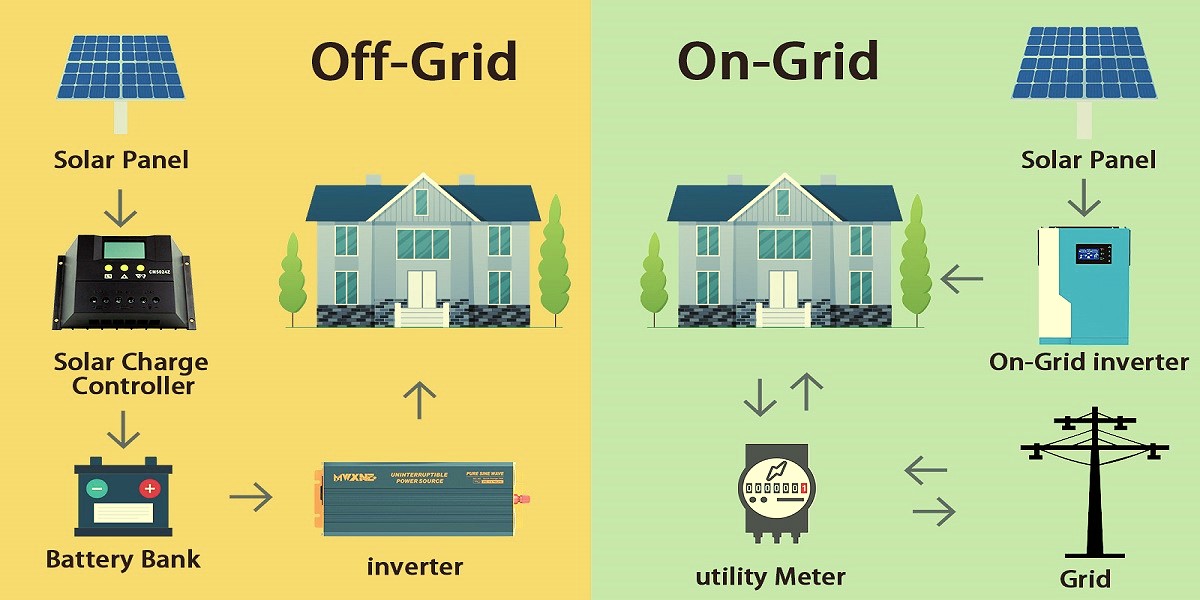
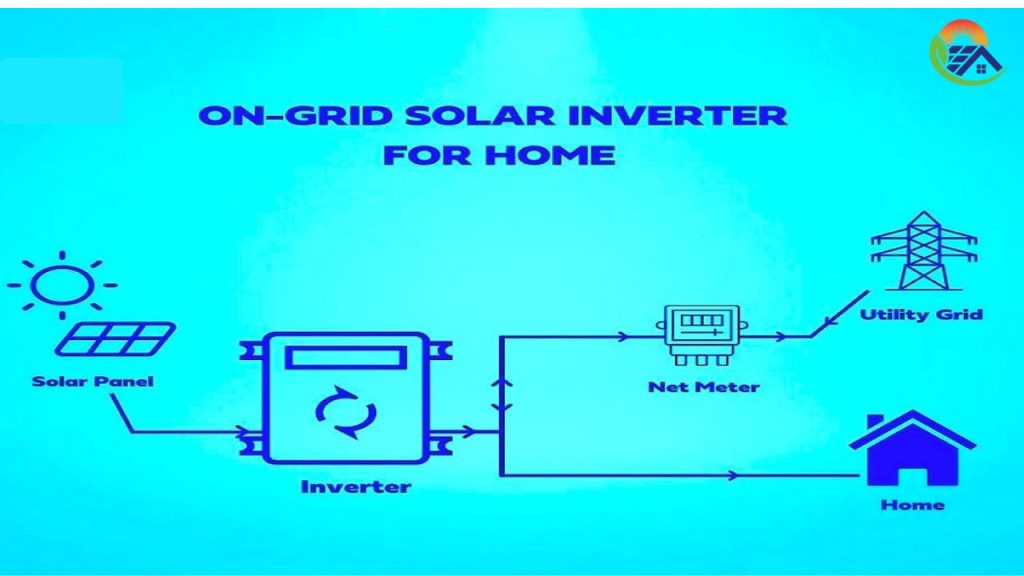
An on-grid inverter, as well known as a grid-tied inverter, is similar to a solar system’s social butterfly. To power your house, it cooperates with the utility grid in your neighborhood. This is how it ends up going:
-
- How It Works: Produces AC electricity for your house from solar DC power. Any extended vitality? Net metering credits are used to feed it back into the grid.
- Important attributes:
- Grid-Dependent: Turns off during shutdowns to uphold utility workers (first and above all, safety!).
- Batteries really aren’t required: use the grid as a backup, that also lowers expenditures.
- Net Metering Friendly: Sell extra energy to the grid to earn credits.
- Ideal For: Homes with trusted grid access in urban or suburban areas. Contemplate it as an outlay partner for reducing electricity costs.
What is an Off-Grid Inverter?
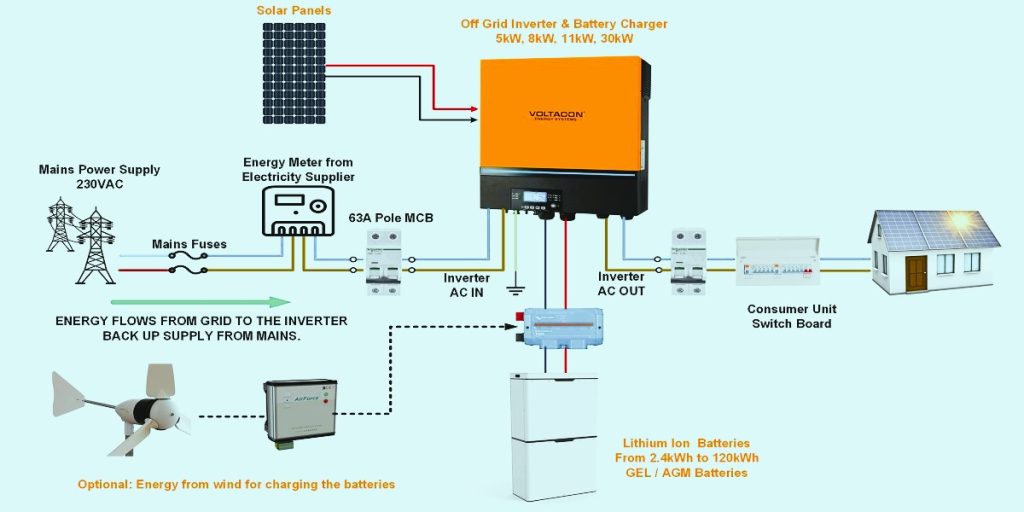
Introducing the harsh idealist of the solar sector, the off-grid inverter. The grid doesn’t really like this inverter. Rather, it runs your residence by itself and is commonly used in combination with batteries for storage.
-
- How It Works:It converts solar DC power to AC whilst also storing extra energy in batteries for use whether at a later time, night or on overcast days.
- Important attributes:
- Energy Independence: Sustains power even when the grid is down.
- Battery Reliant: Increases the initial cost by mandating a battery bank ($$$).
- No Net Metering: Since you are not plugged, you cannot sell back excess power.
- Ideal For: Homes in places with frequent power outages, remote cabins, or motor homes. Ideal for people who appreciate independence over convenience.
6 Key Difference between on grid and off grid inverter
Let’s just get past the technical details and compare these two:
1. Connect to the Grid:
- On-Grid: Needs the grid to operate.
- Off-Grid: Runner autonomously; no grid is required.
2. Storage of Batteries:
- On-Grid: Batteries are rarely used.
- Off-Grid: You’ll require batteries (be ready for sticker shock).
3. Price:
- On-Grid: Less costly up front (no batteries!).
- Off-Grid: More expensive upfront (batteries plus additional parts).
4. Power Failures:
- On-Grid: This anti-islanding safety feature turns off during outages.
- Off-Grid: Keeps running seamlessly grid, no issues.
5. Maintenance:
- On-Grid: Low maintenance.
- Off-Grid: Batteries require routine maintenance.
6. Net Metering:
- On-Grid: Make money by supplying the grid with energy.
- Off-Grid: Store it or lose something on your own.
Side-by-Side Comparison Table: Difference between on grid and off grid inverter
| Feature | On-Grid Inverter | Off-Grid Inverter |
| Grid Connection | Required | Not needed |
| Battery Storage | Rare | Essential |
| Upfront Cost | $ | $$$ |
| Outage Resilience | No | Yes |
| Net Metering | Yes | No |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate-High |
When to Use Each Inverter
Choose On-Grid if
- This same grid power in the city where you live is steady.
- End is your aim, not going entirely green.
- The possibility of obtaining net metering credits appeals to you.
Select Off-Grid if
- You’re kilometers away from the grid and in a remote location.
- You commonly lose power (look at you, areas that are prone to storms!).
- Your mission statement is energy independence.
How to Pick the Right Inverter for You
- What really is my home? No grid in the zone? Your hero is off-grid.
- How Much Do I Have to Spend? Off-grid is more costly but offers more freedom; on-grid saves a lot of money up front.
- What is the importance of backup power? On-grid is effective if outages are infrequent. Go off the grid for peace of mind.
- Also must I Sell Energy? Off-grid keeps it all for themself, while on-grid allows you to make money.
Conclusion
Difference between on grid and off grid inverter: Your location, financial position, and degree of independence versus convenience will all play a role in your decision between and off-grid inverters. While off-grid setups empower adventurers who prefer to venture off the beaten path, on-grid systems are more inexpensive for urban residents.
Really not sure? Speak with a solar installer, and they will configure suggestions to meet your needs. And hey, if you’re still indecisive, power vehicles are always an option.
FAQs
Q: Can I switch from on-grid to off-grid later?
A: Yes, but you’ll need to add batteries and possibly a new inverter. Plan ahead!
Q: Do off-grid inverters work without batteries?
A: Nope! Batteries are non-negotiable for storing solar energy.
Q: Are hybrid inverters worth it?
A: If you want grid perks and backup power, hybrids are a smart investment.
Q: Why do on-grid inverters shut off during outages?
A: Safety first! They prevent sending power to the grid, protecting repair crews.